Monitoring Windows Processes with WMI
In this chapter, you’ll learn how to use WMI to monitor Windows Processes. Nectus lets you create profiles that specify which Processes to monitor with WMI and to send Alerts related to them.
The specific topics we will cover in this chapter are:
- What is WMI?
- Why Monitor Windows Processes?
- Creating a WMI Monitoring Profile
- Editing a WMI Monitoring Profile
- Assigning a Profile to a WMI Server Group
1. What is WMI?
WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) is a set of specifications and interfaces that provides information about the status of local and remote computers running Microsoft Windows. In this chapter we look at how Nectus uses WMI to monitor the status of Windows Processes and send Alerts based on that status.
Note: WMI is the Microsoft implementation of the Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) standard and the Common Information Model (CIM) standard from the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF).
2. Why Monitor Windows Processes?
You will normally want a particular set of Windows Processes running on your servers. Nectus can notify you when these Processes run, ensuring you that everything starts properly. You can also watch for specific Processes you don’t want on your servers.
For example, viruses run as Processes. If you know the names of the Processes associated with a specific virus, Nectus can notify you if any of those Processes starts running on one of your servers.
Monitoring for stopped Windows Processes lets you respond quickly to the failure of an important business Process.
3. Creating a WMI Monitoring Profile
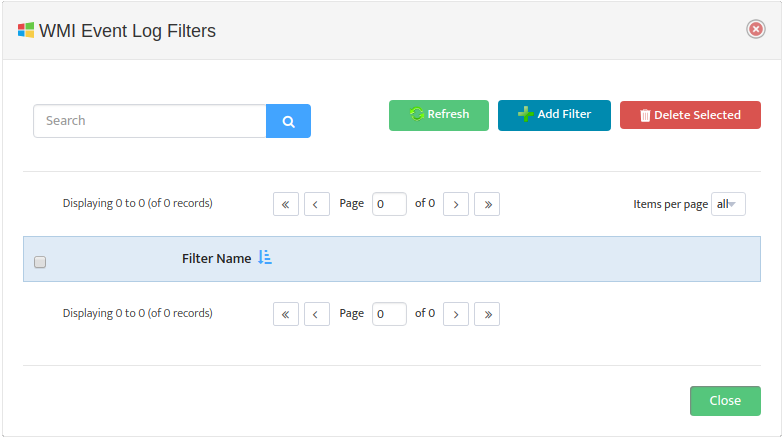
To create a WMI Monitoring Profile go to the Nectus Home Screen and select Monitoring -> WMI Monitoring Settings.
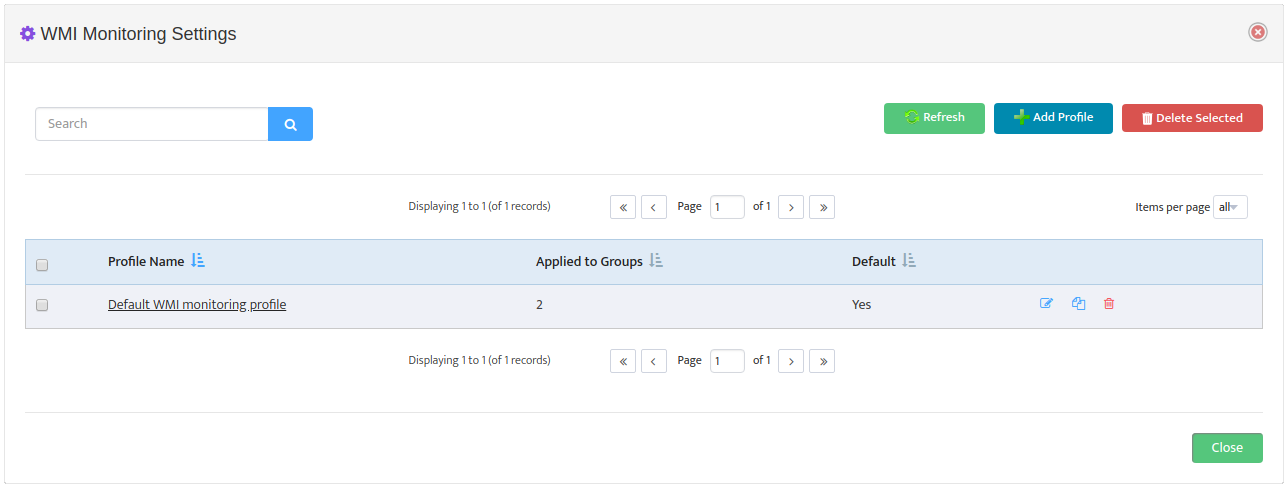
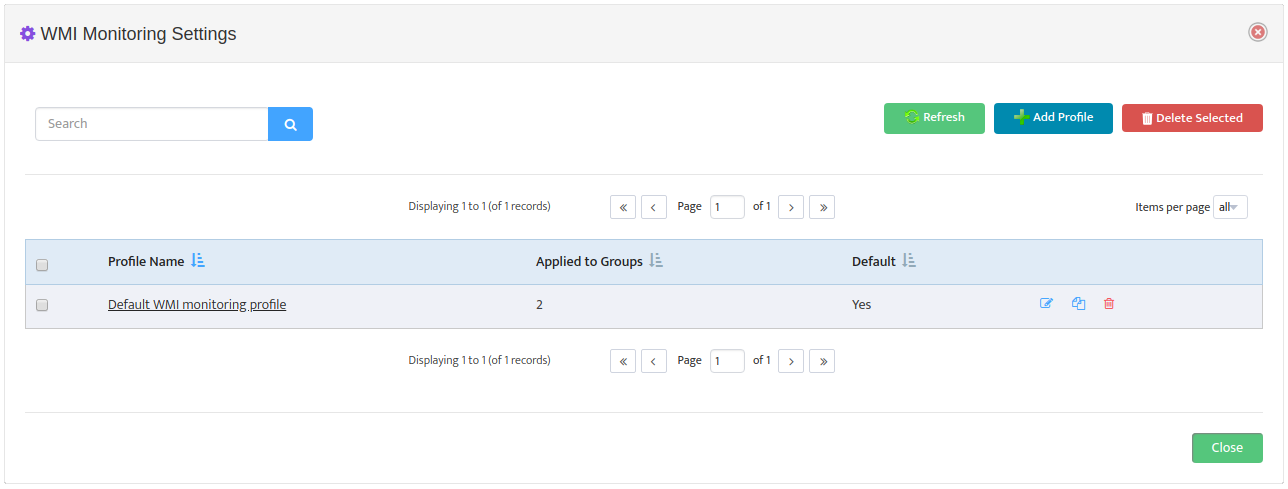
This opens the “WMI Monitoring Settings” dialog box.
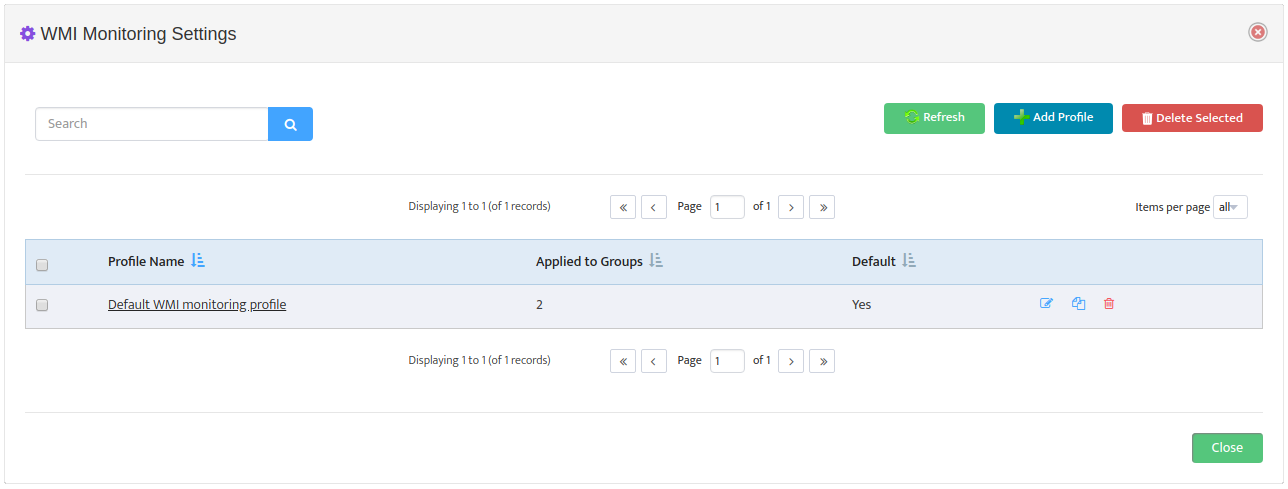
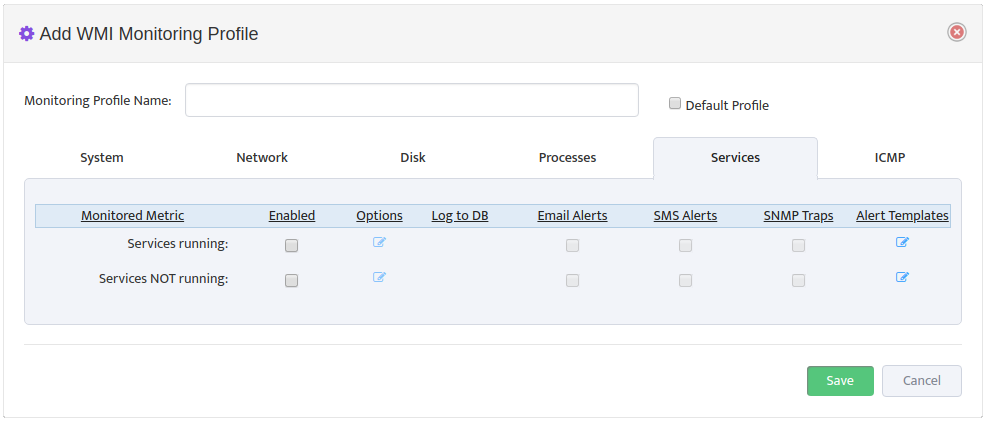
Click Add Profile -> Processes.
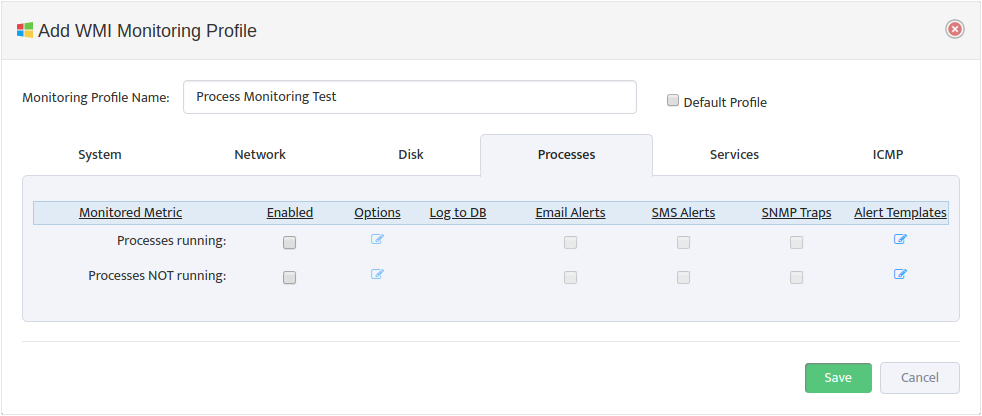
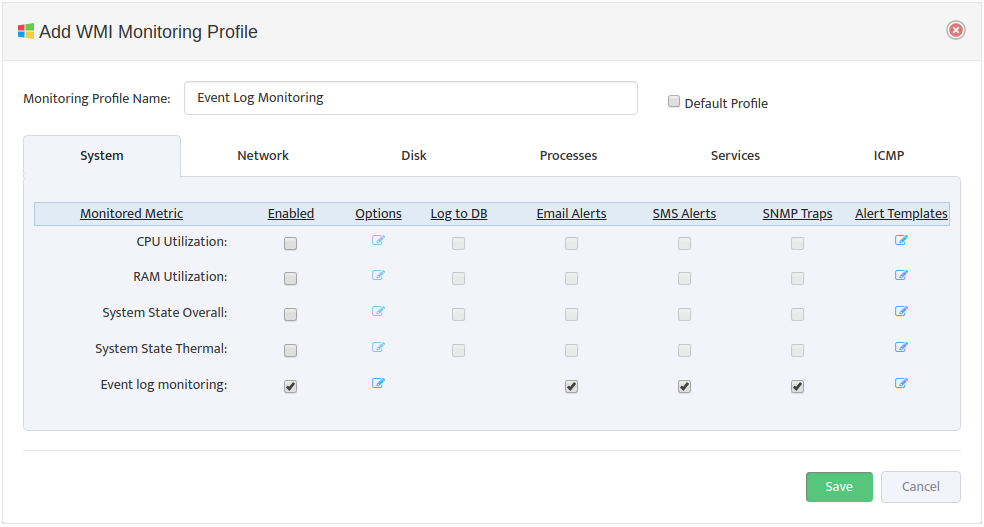
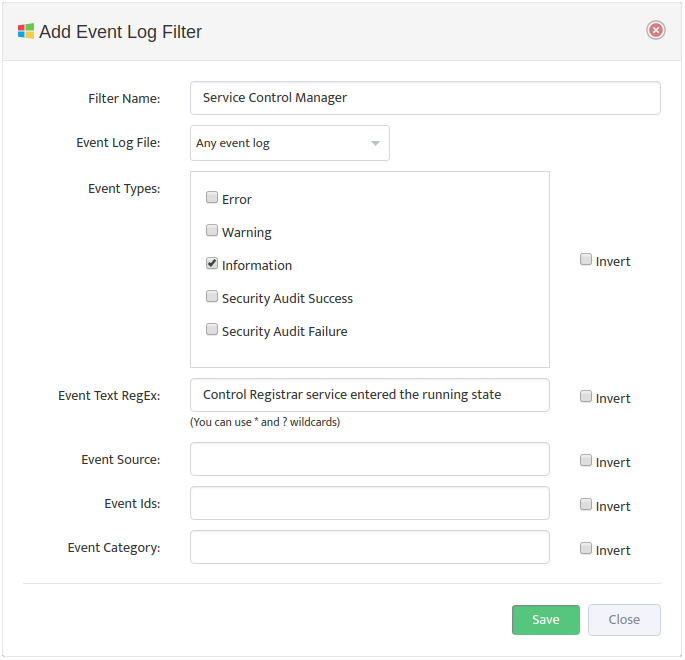
Create a new Profile by entering the Monitoring Profile Name and checking the Enabled boxes next to the metrics you want to monitor. In addition, check the types of Alerts you want to send for each Monitored Metric. See Section 4, “Editing a WMI Monitoring Profile” for details on how to specify which Processes you want to monitor and how you want to be alerted.
Check the Default Profile box if you want to make this the new default WMI Monitoring profile.
4. Editing a WMI Monitoring Profile
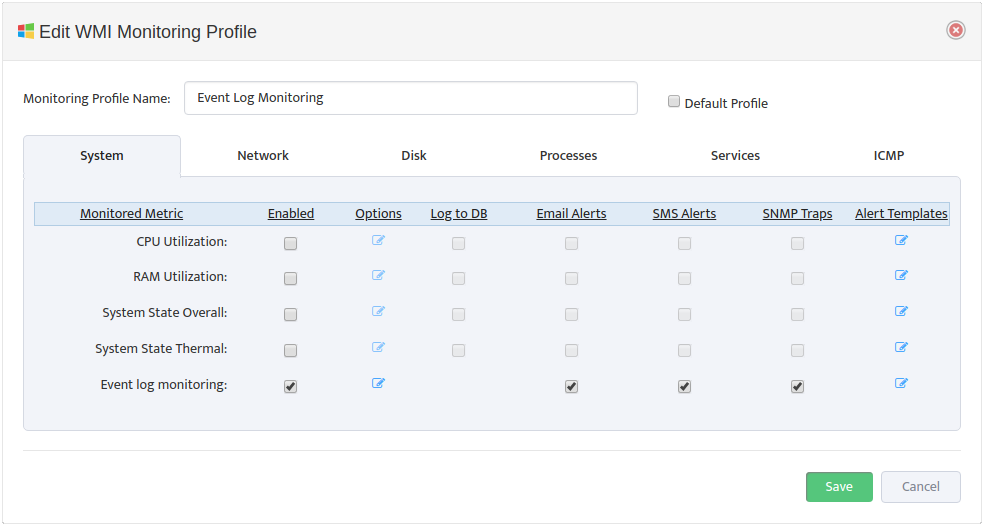
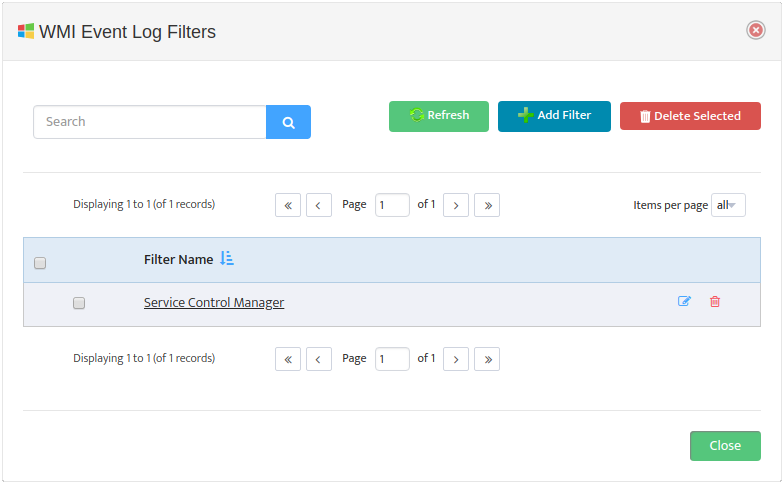
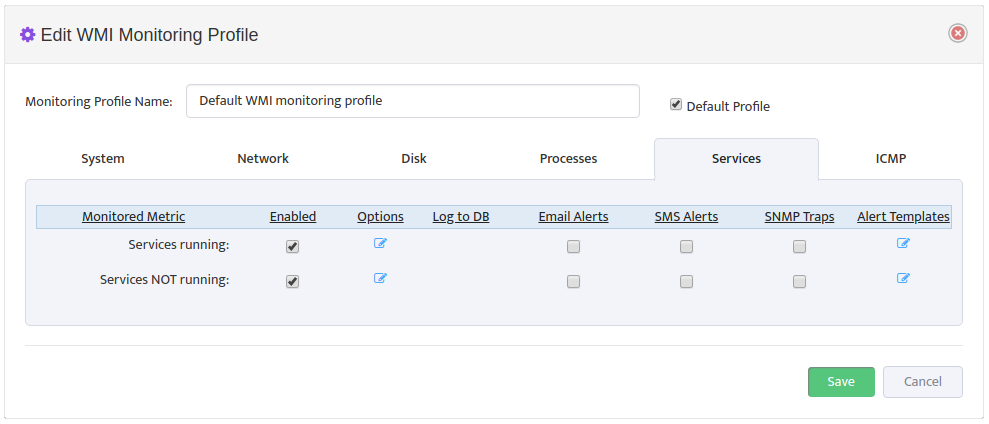
To edit a WMI Monitoring Profile, open the “WMI Monitoring Settings” dialog box and select the Edit Profile icon for the Profile you want to edit. In “Edit WMI Monitoring Profile” dialog box that appears select the Processes tab.
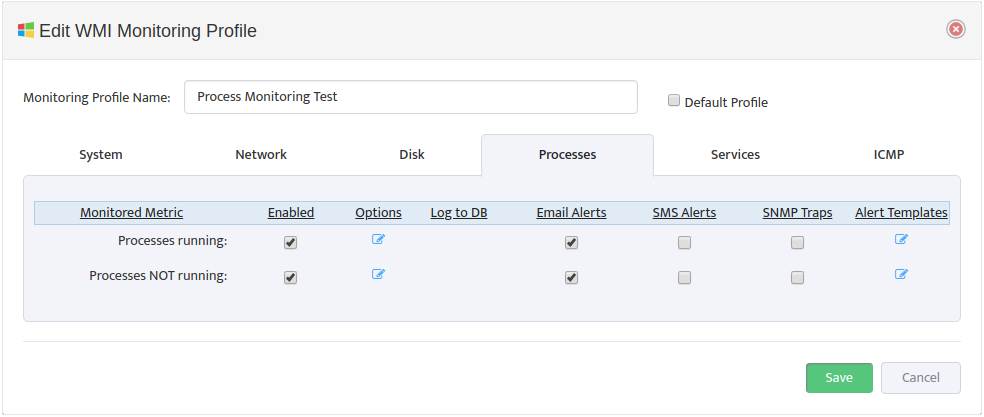
4.1 Editing Options
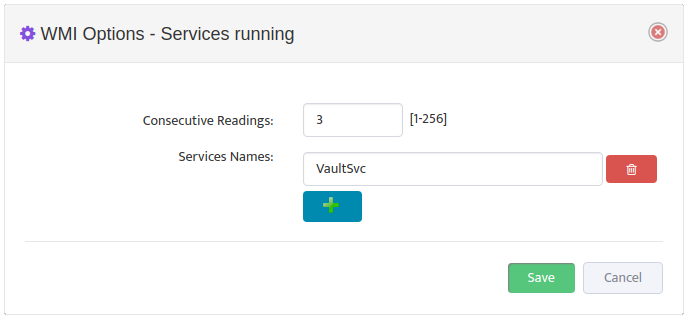
Select the Options icon for the Metric you want to edit to open the “WMI Options” dialog box.
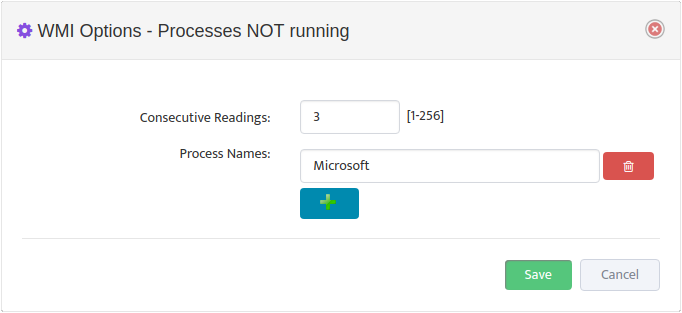
Set the number of Consecutive Readings needed to trigger an alert then click the Add Name button to add the Processes you want to monitor.
4.2 Editing Alerts and Templates
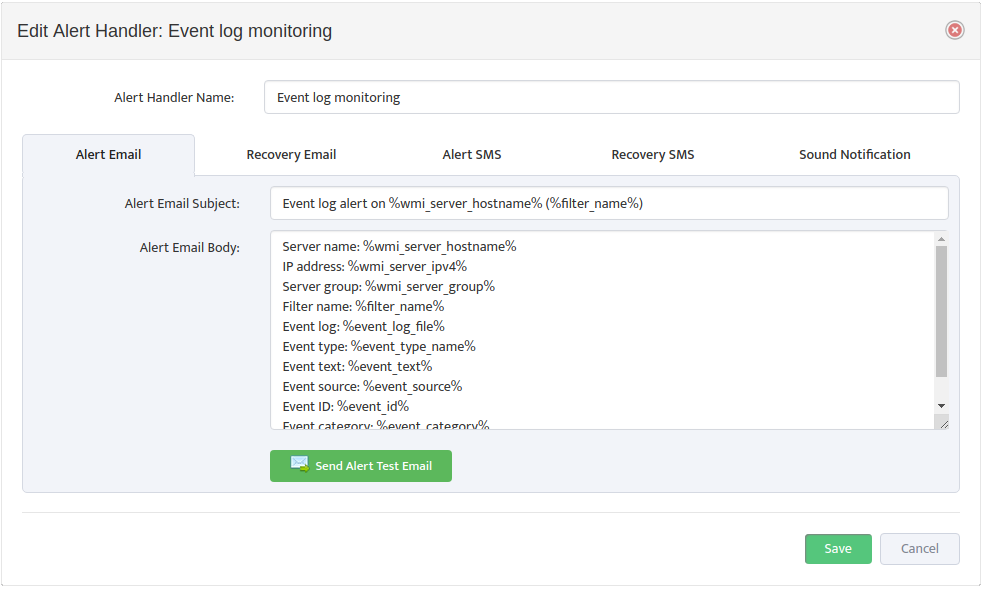
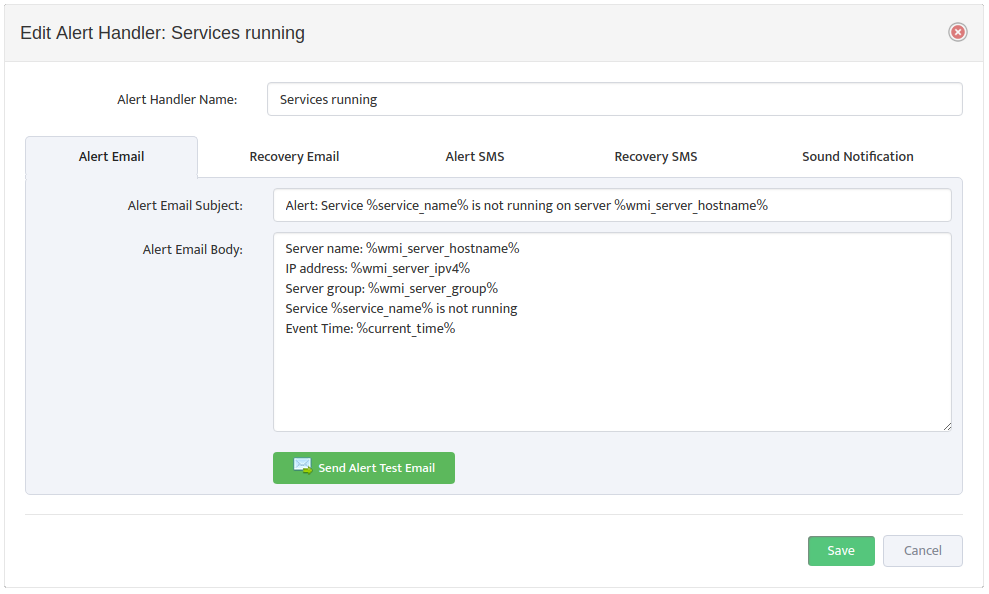
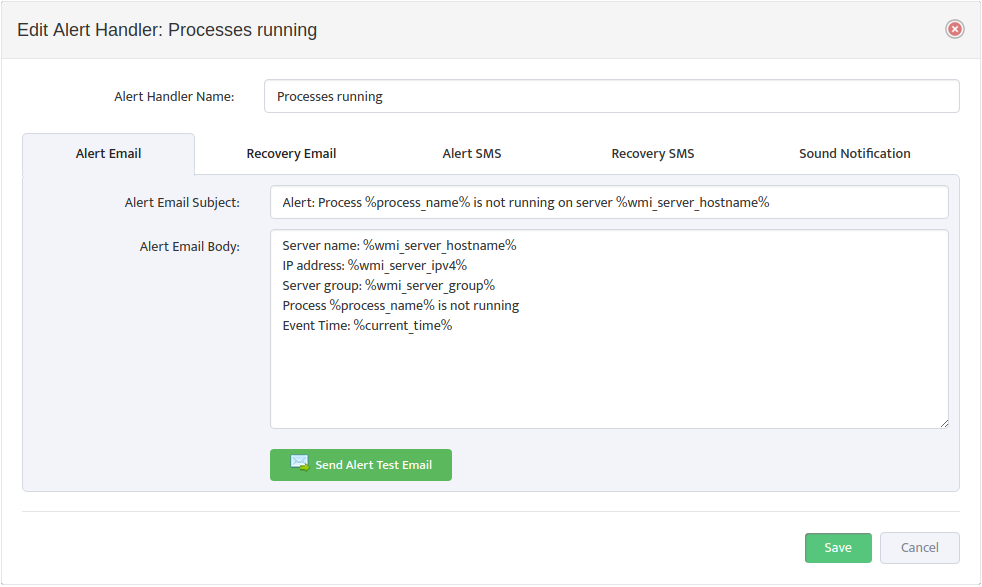
In the Processes tab of the “Edit WMI Monitoring Profile” dialog box, check or clear the types of Alerts to send for each Monitored Metric. To edit the format of the Alerts, open the “Edit Alert Handler” dialog box by clicking the Edit Alert Templates icon.
5. Assigning a Profile to a WMI Server Group
In the WMI Servers Panel on the Nectus Home screen, open the WMI Servers list. Right-click a WMI Server Group and select Properties.
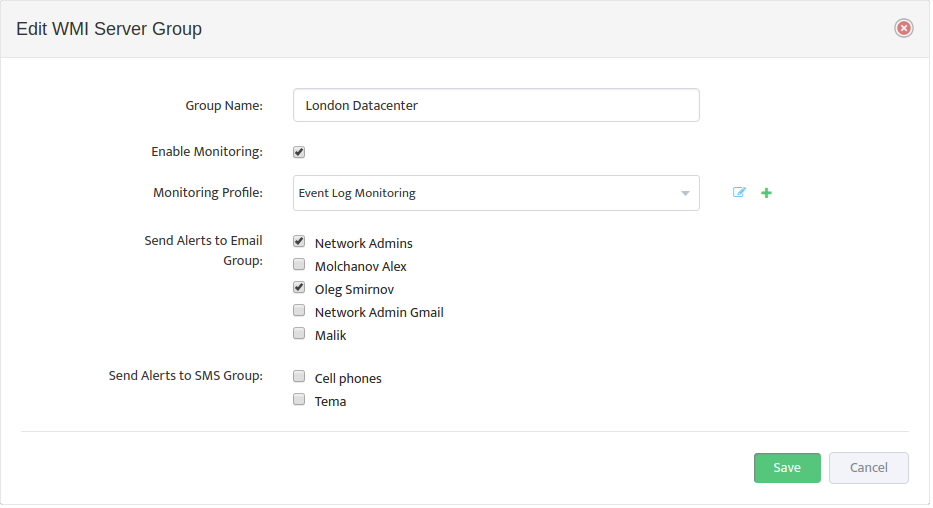
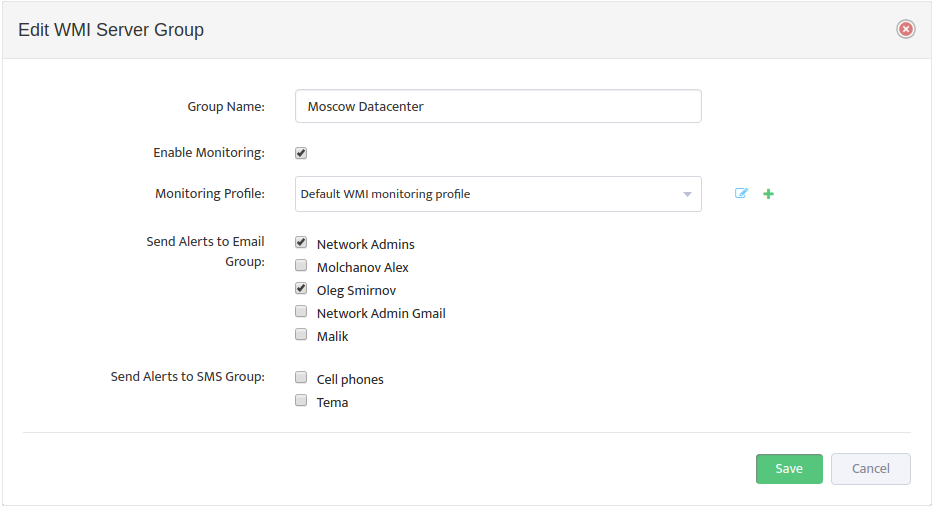
This opens the “Edit WMI Server Group” dialog box.
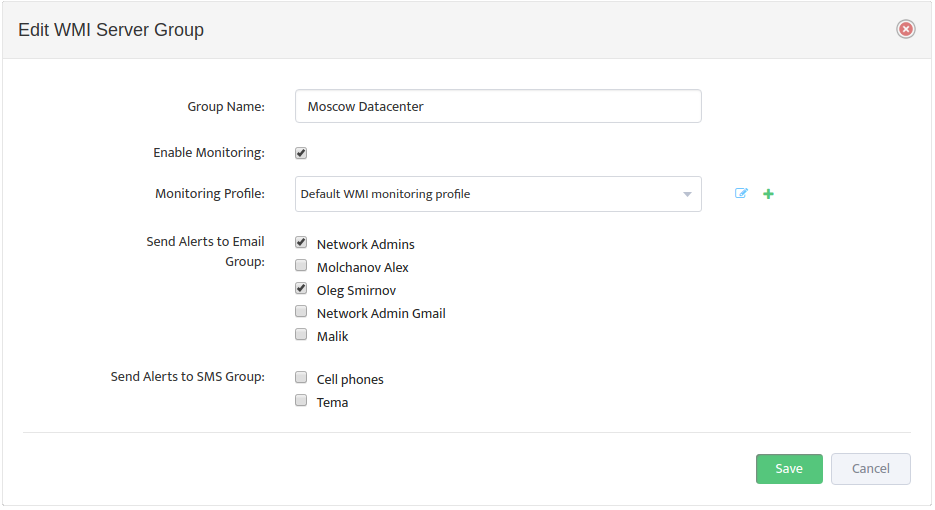
Check the Enable Monitoring box, then select the WMI Monitoring Profile to use from the Monitoring Profile drop-down list, and specify which groups will receive the Alerts.
The icons to the right of the Monitoring Profile list allow you to edit a Profile or add a new Profile directly from here.