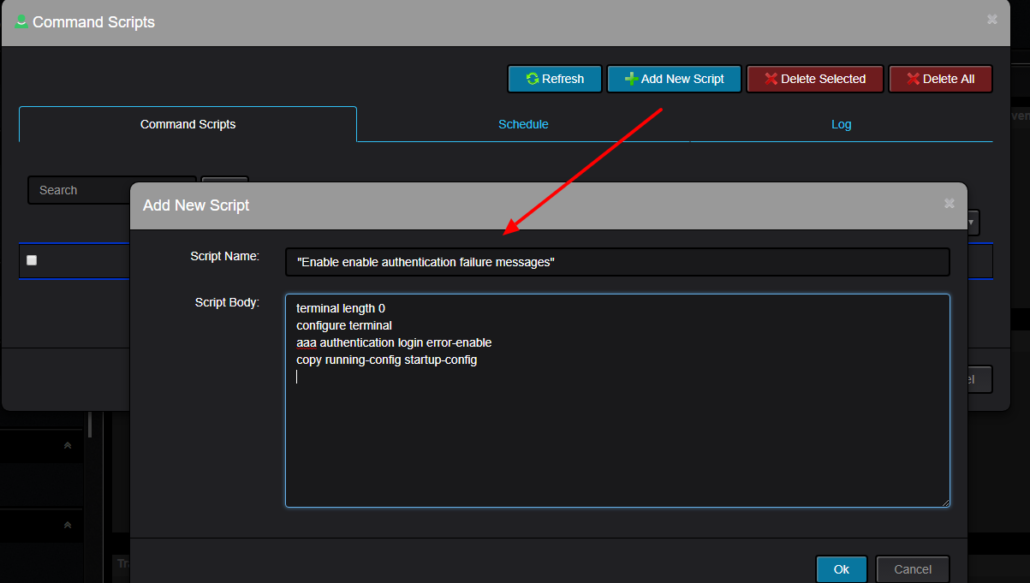
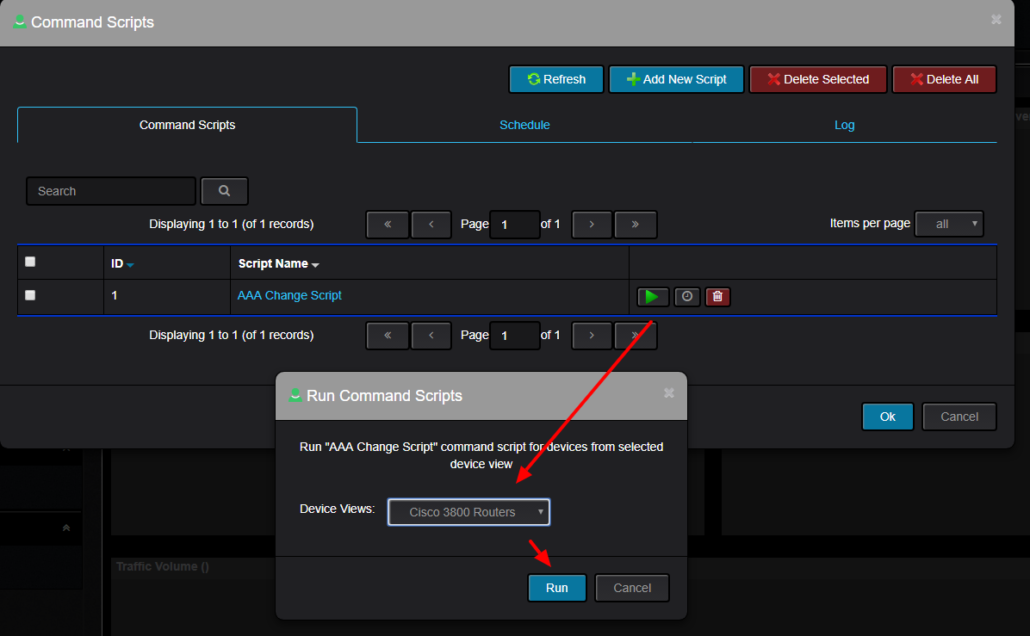
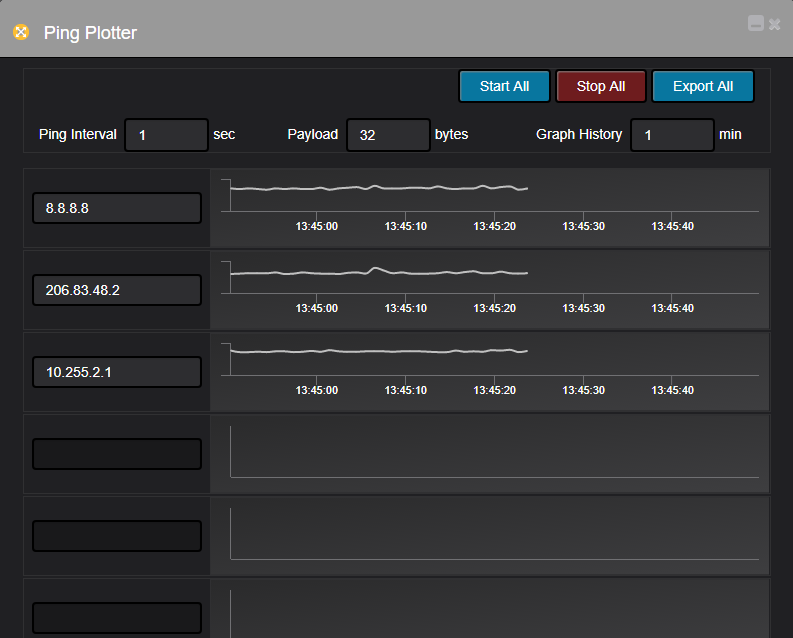
This is an example on how to obtain list of IP addresses assigned to Interfaces inside specific SNMP Context on Nexus 7000
Step 1.
Obtain list of all SNMP Contexts by sending SNMP GET Bulk for cContextMappingVrfName (.1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.468.1.1.1.2)
Response:
‘1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.468.1.1.1.2.10.109.97.110.97.103.101.109.101.110.116’=>”management”
In this response Nexus 7018 Switch has only one SNMP context with a name “management”
Step 2.
Obtain list of all IP addressses that exist in context “management” by sending SNMP GET Bulk for ipAdEntIfIndex (.1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.2)
Note that for this step step we have append context name to V2 community string
(e.g public@management) to specify that this request is specific for context “management”.
Response:
‘1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.2.10.255.27.34’=>”83886080″
In this response we have IP address [10.255.27.34] and associated interface ifIndex “83886080”
Step 3.
Find interface name with ifIndex 83886080 by sending SNMP GET Bulk for (.1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2)
Response:
‘1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2.83886080’ => “mgmt0”
So in these 3 steps we have found that Interface Mgmt0 has assigned an ip address 10.255.27.34